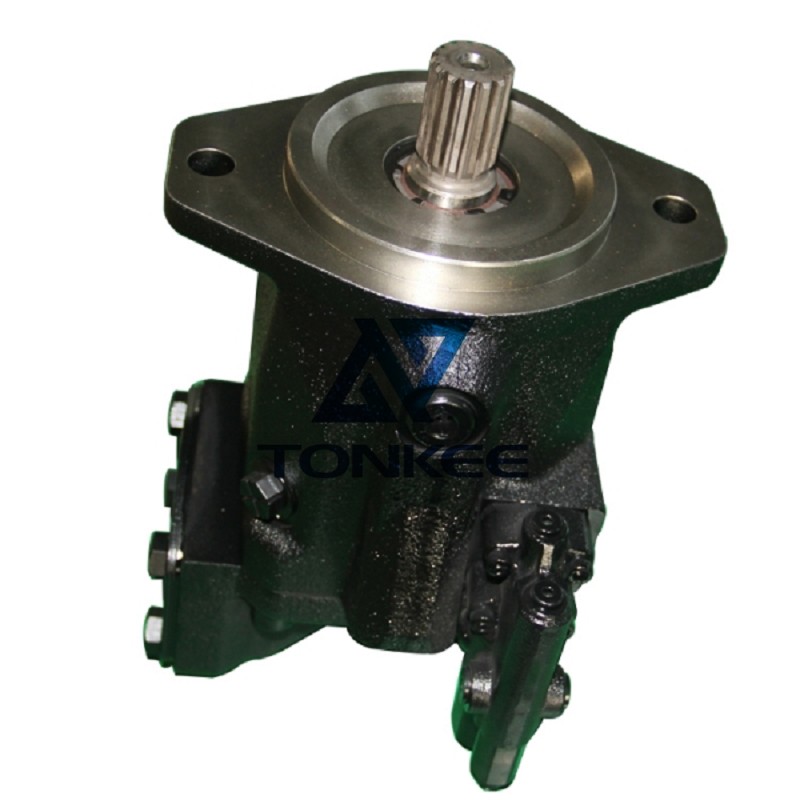
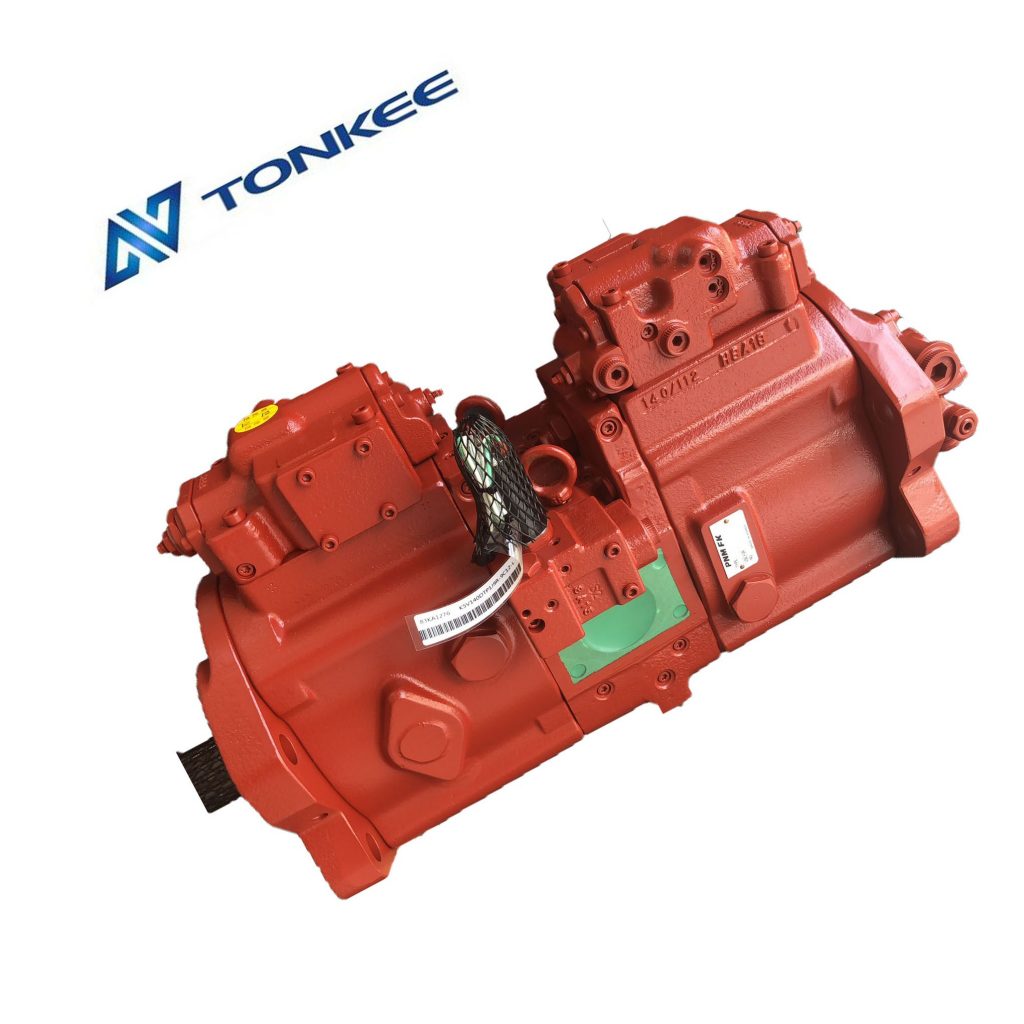
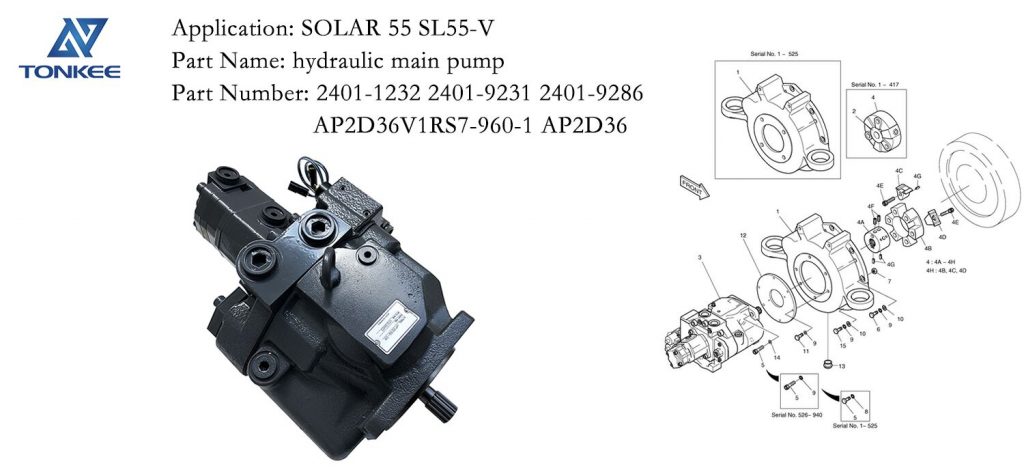
Pump Type: Piston pumps can be categorized into various types, including axial piston pumps, radial piston pumps, and inline piston pumps.
The specific type may vary depending on the application.
Flow Rate: This refers to the volume of fluid the pump can move in a given period. It is usually measured in liters per minute (LPM) or gallons per minute (GPM).
Pressure Rating: The maximum pressure that the pump can generate. It is typically measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or bar.
Material: The pump's construction material is essential, especially if it will handle corrosive or abrasive fluids. Common materials include stainless steel, cast iron, or various types of alloys.
Piston Diameter: The diameter of the piston or pistons used in the pump, typically measured in millimeters (mm) or inches (in).
Stroke Length: The distance the piston travels back and forth within the cylinder.
Drive Mechanism: Some piston pumps are powered by electric motors, while others may use hydraulic or pneumatic systems. The drive mechanism is essential for understanding how the pump operates.
Seals and Gaskets: Details about the seals and gaskets used in the pump, which are crucial for maintaining fluid integrity and preventing leaks.
Operating Temperature Range: The range of temperatures within which the pump can operate effectively and safely.
Efficiency: Information about the pump's efficiency, which can impact energy consumption and performance.
Mounting Configuration: How the pump is designed to be mounted or installed within a system.
Inlet and Outlet Connections: The size and type of connections for fluid intake and discharge.
Maintenance Requirements: Information about maintenance intervals and procedures for the pump to ensure its longevity and reliability.
Optional Features: Some piston pumps come with optional features like pressure relief valves, variable displacement, or integrated filters.
Compliance and Certifications: If applicable, certifications for safety or quality standards that the pump meets.



 English
English Русский язык
Русский язык