AP5S53 and AP5S67 are most likely part numbers or designations used in industrial or automotive applications.
These alphanumeric codes are often used to identify specific components, and without more context, it's challenging to provide detailed specifications for these parts. The specification for these parts would include information such as dimensions, material composition, load-bearing capacity, and compatibility with other components in a system. It's essential to consult the manufacturer or reference their documentation to obtain precise specifications for these components.
HMSF072:
HMSF072 appears to be another part number or designation, likely for a specific component in a mechanical or industrial system. Detailed specifications for HMSF072 would typically include information about its dimensions, material composition, torque or power ratings, operational parameters, and any specific use or application guidelines. Without additional context or access to specific documentation, it's challenging to provide detailed specifications for HMSF072.
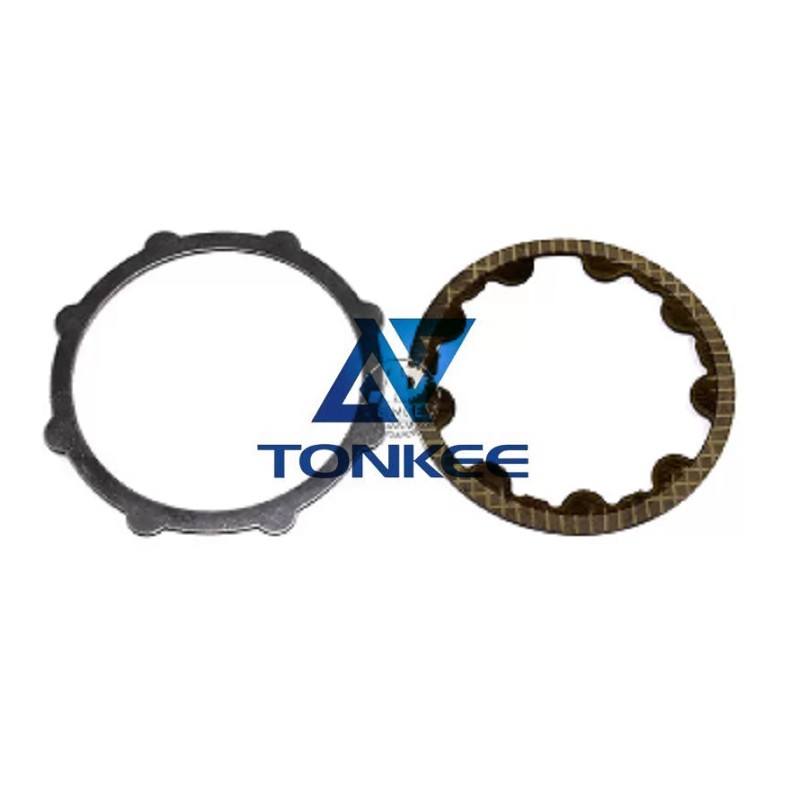
Friction Separation Plate:
A friction separation plate is a critical component used in various mechanical and automotive systems.
Its primary purpose is to control or modulate the transmission of power between two rotating components. This is achieved through the friction generated by the contact between the plate and adjacent components. Here are some general specifications for a friction separation plate:
Material: Friction separation plates are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials, designed to withstand the stresses and temperatures of the system in which they are used.
Dimensions: The dimensions of the plate, including its diameter, thickness, and outer shape, are crucial to ensure it fits properly within the system.
Friction Coefficient: The friction coefficient of the plate's material is a key parameter that determines its effectiveness in transmitting or limiting power transfer.
Operating Temperature Range: The plate should be designed to operate within a specific temperature range to maintain its performance and integrity.
Load-Bearing Capacity: The plate should be rated to handle a particular load, ensuring it doesn't wear prematurely or fail under stress.
Compatibility: It should be compatible with the other components in the system, such as a clutch, brake, or gearbox.



 English
English Русский язык
Русский язык